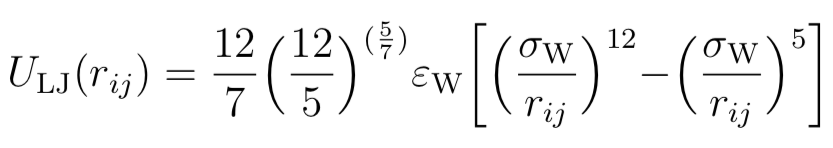SPICA: Surface Property fItting Coarse grAined model
Force Field
pSPICA Force Field
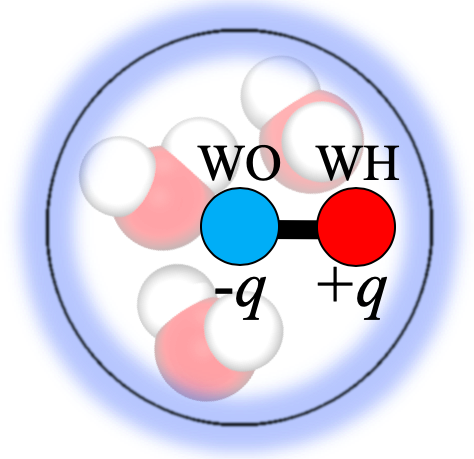
pSPICA is a CG force field developed with a "polar" CG water model. The CG modeling scheme in pSPICA is almost the same as that in the SPICA FF. The full details of pSPICA can be found in the publication. The pSPICA FF is developed using the polar CG water model containing a dipole within the particle as shown below.The polar CG water model composed of a pair of interacting sites, WO and WH, is designed to represent three water molecules in aqueous solution. The two sites, WO and WH, are connected by a rigid bond and carry negative and positive partial charges, respectively. Nonbonded interaction is described by a Lennard-Jones (LJ) interaction and the electrostatic interaction. WH site only carries partial charge, though WO throughthe LJ interaction using the following LJ12-5 function:
where εW and σW are LJ parameters. The prefactor of the LJ12-5 function is decided to have the minimum value as -εW and to attain zero at rij = σW. This functional form and the LJ parameters are optimized to reproduce the experimental density, surface tension, and dielectric permittivity of water.
For electrostatic interactions in pSPICA, the relative dielectric constant (εr) = 3.2 is used. Different from the SPICA FF, the charge values given in the topology file are not scaled by the square-root of relative dielectric constant (εr) = 3.2. So the relative permittivity value should be given in the job control script explicitly.
Most of the bonded interactions and the other nonbonded interactions in pSPICA are similar to those in the SPICA FF, though many of pair interaction parameters were reoptimized for pSPICA water. Thus, we have a separate parameter file for pSPICA FF.
Tutorial for pSPICA FF
SPICA Force Field
Okayama University